What is a Gas Transfer Pump?
A gas transfer pump is a precision-engineered device designed to move gases—such as industrial gases, compressed gases, and cryogenic liquids—safely and efficiently between storage vessels, transport containers, and distribution systems. These pumps ensure product purity, minimize heat ingress, maintain operational safety, and deliver precise pressure and flow control under a variety of conditions.
Gas transfer pumps are critical in industries ranging from industrial gas production and medical gas supply to LNG fueling and cryogenic applications. Depending on design and functionality, they may also serve as gas filling pumps, liquid gas pumps, gas motor pumps, or cryogenic vacuum pumps.
Types of Gas Transfer Pumps
Gas transfer pumps are specialized pumps designed for the safe and efficient movement of various gases, including cryogenic liquids, under specific conditions. They are classified based on their working principles and operating methods.
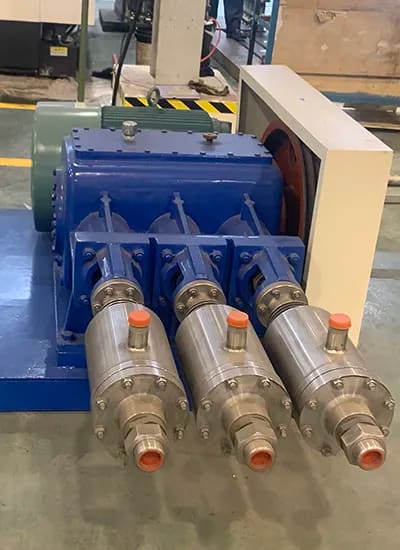
1. Piston Gas Transfer Pumps
- Operate using a reciprocating piston mechanism.
- Provide high pressure and precision for applications such as cylinder filling, pipeline pressurization, and fueling systems.
- Common in LNG fueling stations and industrial gas cylinder filling.
2. Centrifugal Gas Transfer Pumps
- Use a rotating impeller to impart energy to the gas or liquid.
- Deliver continuous, smooth flow at moderate pressures.
- Widely used in LNG transfer, ship-to-shore operations, and large-scale storage systems.
3. Submersible Gas Transfer Pumps
- Installed inside the gas or liquid storage tank, fully immersed.
- Minimize heat ingress and eliminate long suction lines.
- Frequently used in LNG terminals, LNG bunkering, and fueling systems.
4. Bath-type Gas Transfer Pumps
- The pump head is immersed in a liquid bath to maintain extremely low temperatures during operation.
- Ensures stable cooling and minimal thermal losses.
- Suitable for high-duty continuous transfer applications.
5. Closed-cycle Gas Transfer Pumps
- Operate with a controlled thermal cycle where the pump is cooled by the same gas or liquid it transfers.
- Designed for long-term, reliable operation with reduced maintenance.
6. Hybrid Gas Transfer Pumps
- Combine features of piston and centrifugal designs.
- Offer both high pressure and high flow capacity, depending on system requirements.
- Applied in flexible operations where both precision filling and bulk transfer are needed.
Comparison of Gas Transfer Pump Types
| Type of Pump | Working Principle | Main Features | Typical Applications | Key Advantages |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Piston Pump | Reciprocating piston compresses and transfers cryogenic liquid | Provides high discharge pressure, precise metering | Cylinder filling, LNG fueling stations, pipeline pressurization | High precision, suitable for high-pressure operations |
| Centrifugal Pump | Rotating impeller imparts kinetic energy to liquid | Delivers continuous, smooth flow at moderate pressures | Bulk LNG transfer, ship-to-shore LNG operations, storage tank transfer | High flow rate, continuous duty, efficient for large volumes |
| Submersible Pump | Fully immersed inside the cryogenic tank | Eliminates suction line losses, minimal heat ingress | LNG terminals, LNG bunkering, fueling systems | High reliability, reduced risk of vapor lock, compact installation |
| Bath-type Pump | Pump head cooled by immersion in a cryogenic liquid bath | Maintains extremely low operating temperatures | Continuous-duty LNG/LOX/argon transfer in industrial plants | Stable cooling, consistent performance, low wear |
| Closed-cycle Pump | Pump cooled by circulating the cryogenic liquid it transfers | Controlled cooling cycle for durability | Long-term cryogenic transfer systems, industrial gas plants | Long service life, reduced maintenance, high reliability |
| Hybrid Pump | Combines piston and centrifugal mechanisms | Offers both high flow and high pressure | Flexible operations requiring bulk transfer and precise filling | Versatile, multi-purpose solution |
How Cryogenic Transfer Pumps Work
A cryogenic transfer pump is engineered to move extremely cold liquefied gases—such as liquid nitrogen (LN₂), liquid oxygen (LOX), liquid argon (LAr), liquid natural gas (LNG), and liquid hydrogen (LH₂)—from storage vessels to transport containers, distribution systems, or end-use applications.
The operation of these pumps involves several critical principles to ensure efficiency, safety, and product integrity:
Core Working Principles
- Low-temperature handling:
Cryogenic pumps operate at temperatures far below –150 °C, requiring specialized materials (stainless steel, nickel alloys) and precision engineering to prevent material embrittlement and ensure safe operation. - Minimized heat ingress:
To prevent vaporization of the cryogenic liquid during transfer, pumps are designed with insulation systems, vacuum jackets, or submersible arrangements to reduce heat transfer. - Pump Types and Mechanisms:
- Piston Pumps: Use reciprocating pistons to compress and transfer liquid, delivering high-pressure flow with precise control.
- Centrifugal Pumps: Use rotating impellers for continuous flow at moderate pressure, ideal for bulk transfer.
- Submersible Pumps: Fully immersed inside the cryogenic liquid for reduced heat loss and suction efficiency.
- Bath-type Pumps: Utilize a cryogenic liquid bath to keep pump heads cooled for stable performance.
- Closed-cycle Pumps: Use the transferred cryogenic liquid for their own cooling cycle, enhancing efficiency.
- Hybrid Pumps: Combine piston and centrifugal principles to meet both high-pressure and high-flow requirements.
- Sealing Systems:
Cryogenic transfer pumps employ advanced sealing solutions (mechanical seals, bellows seals, or magnetic couplings) to prevent leaks, ensure safety, and maintain low temperatures.
Key Applications of Gas Transfer Pumps
Cryogenic transfer pumps are essential in industries where safe, efficient, and precise movement of cryogenic liquids is required.
- LNG Industry: Ship-to-shore transfer, LNG bunkering, storage tank refilling.
- Industrial Gas Production: Transfer of LOX, LN₂, LAr for manufacturing, welding, electronics, and chemical processes.
- Medical Industry: Liquid oxygen filling systems for hospitals and healthcare facilities.
- Research & Laboratories: Cryogenic supply for superconducting magnets, particle accelerators, and cryogenic experiments.
- Energy Sector: Hydrogen fueling stations, LNG fueling, and energy storage applications.
- Aerospace: Transfer of liquid hydrogen and oxygen for rocket fueling and propulsion testing.
Advantages of Gas Transfer Pumps
- Minimized product loss due to reduced boil-off gas during transfer.
- High efficiency and reliability in low-temperature environments.
- Versatility across different gases and pressures.
- Enhanced safety through advanced sealing and insulation systems.















No comment